Cloud computing modifies the operations of technology companies, opens new opportunities for industry, and provides growth and business improvement. Cloud technologies enable storing, processing, and managing huge amounts of data in real time, across numerous servers. Thus, a software solution can be accessed anytime, from any device or browser.
We use cloud technologies on a daily basis without knowing it. For example, your team may employ Google Docs instead of exchanging Microsoft Word documents through email. It is a fast, simple, and convenient way to improve the teamwork.
There are several types of cloud computing technologies, and today, we will discuss SaaS meaning and compare it to other cloud computing categories.
What is Software-As-A-Service (SaaS)?
What is the software-as-a-service (SaaS) model? This is a cloud-computing category that assumes leasing access to a ready-made software solution through the internet.
The idea of SaaS appeared in the late 1990s. At first, it was simply a concept without real applications. However, in recent years, the situation changed. A number of SaaS vendors appeared; hundreds and thousands of business owners worldwide have risen their capitals thanks to this model. According to Statista forecast, the SaaS market is expected to rise up to almost $133 billion by 2020.
What does SaaS mean? Software as a service definition states that SaaS is a model of using business applications in the format of internet services. SaaS applications run on the provider’s server and users access them using any internet-connected device. The user does not buy the SaaS application, but rents it – pays a certain amount per certain period to use it.
The major advantages of this sales model are:
- Lower ownership cost;
- Shorter deployment terms;
- Low entry threshold and the possibility to try the software free of charge;
- Support, update, and maintenance are the responsibility of the vendor;
- Worldwide access;
- Possibility to connect distributed offices and remote staff;
- Minimal requirements for the user hardware;
- Cross-platform capabilities.
Traditional Software vs. Software as a Service
What are the key differences between traditional on-premise hosted software and SaaS? Here are five points concerning this question:
1. Purchasing
To start cooperating with the SaaS vendor, you need to pay a periodical fee for their services. Most of the established providers also propose a variety of trial periods/schemes, allowing to test the solution beforehand.
A traditional app assumes two variants – customer either buys ready software that would be further customized to their needs after the installation or orders the development from scratch. The third among most used – subscription model – assumes the periodical fees similar to SaaS. The difference here is that any customizations require extra payments.
2. Hosting
Starting your cooperation with the SaaS vendor, you can forget about hosting costs and issues. Your partner handles all the related operations.
Traditional products require hosting costs. In the case of the on-premise deployment, this incurs the cost of servers and network infrastructures, their support, and maintenance. If the software is deployed to external hosting, additional costs are constituted by hosting and software support fees.
3. Maintaining
SaaS Business model is based on subscription. The initial costs are relatively low; besides, service providers offer attractive discounts and benefits for long-term cooperation.
Supporting traditional software requires a lot of additional payments. For example, each update, new users, extra module or bugfix will cost you extra.
4. Backing the data up
SaaS vendors take care of regular backups. In case of any trouble, you will have a chance to roll back painlessly.
Taking care of reservation in traditional solutions is the responsibility of your staff.
5. Security
All the established SaaS providers have tried and tested security strategies and experts.
Building a traditional app, the development team must be experienced enough to employ the latest information security methods and keep the product safe.
SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS
Now when we explained what is SaaS business model, it is time to get acquainted with another cloud computing-based software distribution models. So, IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS: what do these abbreviations mean, what are their key features, and how to choose a fitting option for your next project?
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Cloud providers of this type provide their customers with the ability to construct a virtualized network environment consisting of such elements as servers, routers, switches, other network devices, interconnections, storages, operating systems, programs, etc. IaaS is a great alternative to buying expensive hardware for the deployment of a certain software ecosystem. IaaS user gets full control over the entire virtualized data center in the cloud, including additional services like monitoring, a collection of operational data, log analysis, backup, replication, and recovery.
IaaS features:
- Full range of services of a complete networking infrastructure;
- High scalability, flexibility, and dynamic resource regulation;
- Full control over the infrastructure;
- Costs of the services depend on resource consumption.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS products are the cloud frameworks used by engineering specialists as the basis for custom software. A development team fully manages an app while servers and physical infrastructure are provided by the PaaS vendor. This model allows IT specialists to fully focus on a solution they build instead of solving infrastructure issues.
PaaS and SaaS have much in common. The main difference is that SaaS provides ready apps while PaaS provides the tools for the development and deployment of software.
PaaS features:
- Impressive scalability;
- A huge number of services for software development and testing;
- Integration with multiple third-party web services.
What is the difference between IaaS PaaS and SaaS?
| Purpose | Key Advantages | Examples | |
| IaaS | Access to a complete virtualized networking environment |
|
Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Compute Engine |
| PaaS | Software development and deployment |
|
Heroku, Force.com, OpenShift |
| SaaS | Access to software products from any device connected to the World Wide Web. |
|
Salesforce, Dropbox, Slack |
Examples of SaaS Models
To help our readers to better understand the concept of SaaS, we reviewed some of the popular products that represent this category:
Nimble
Nimble works for you by automatically combining your Office 365 contacts, communication histories, email inboxes, and calendar appointments with over 160 SaaS business app contacts and social media connections (Linkedin, Twitter, Facebook) into one unified team relationship manager.

Google Drive/Google Docs
Google provides customers with highly secure personal and corporate file storages. Files, stored in Google Drive can be accessed from any internet-capable device. Thanks to the direct integration with Google Docs, documents stored in Drive can be edited in place. Moreover, the service provides wide capabilities for collaboration.

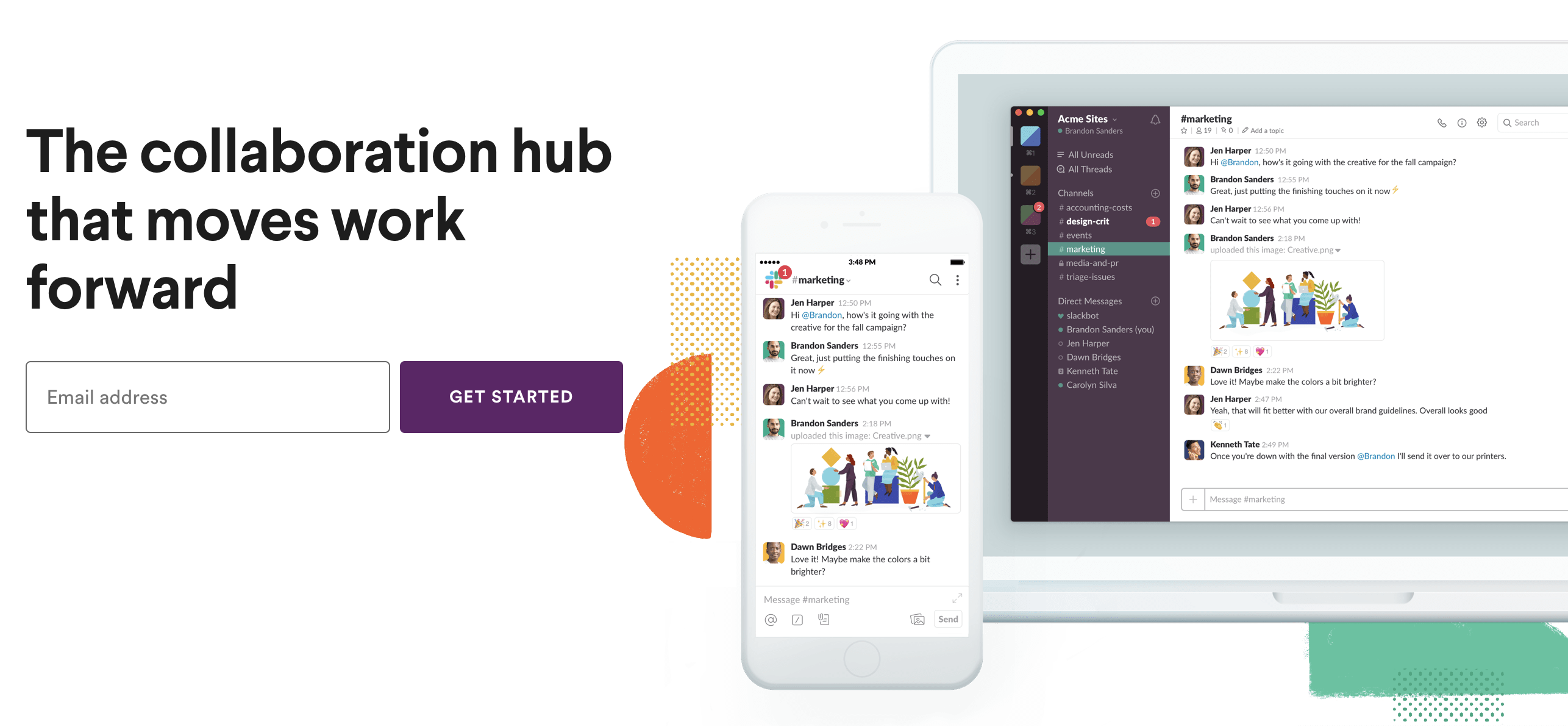
Slack
Modern team communication would be completely different without Slack. Convenient conversations, secure messaging and file sharing are available thanks to this great SaaS product. Features, first used in Slack are currently copied by most of the companies providing the tools for corporate messaging.
Conclusion
Cloud computing keeps revolutionizing IT industry. Its categories provide immense opportunities for a variety of businesses and experts. SaaS products have the strongest impact as millions of users worldwide experience the advantages and convenience of SaaS products daily.